Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) / Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
The DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) and SLM (Selective Laser Melting) technologies belong to the same group of 3D printing technologies: powder bed technologies. Both technologies enable 3D printing in the metal of the currently most popular metal alloys. Technologies differ only in certain technical solutions that are patented by one manufacturer or the other.
The 3D printing process is similar to SLS technology. An alloy powder of the selected metal is the feedstock. In metal Additive Manufacturing technologies it is required to use supporting structures to connect the built model with the machine platform and for certain geometry angles for the built part. The supporting structure is designed to support a given structure but also helps in the proper dissipation of thermal energy. The most commonly used layer thicknesses in metal 3D printing technologies is 30-60 µm.
What are the benefits of DMLS / SLM?

Benefit #1
Parts weight optimization - topology

Benefit #2
Geometric structures production that can be made only by 3D printing - e.g. cooling channels for tools (conformal channels)

Benefit #3
Difficult-to-cut materials processing - e.g. nickel alloys

Benefit #4
Meeting high-quality requirements for advanced industries - aviation, medicine
Materials
These are alloys based on the ALSi10Mg and AlSi7Mg0.6 from casting. 3D printed parts made of this material are often used as functional prototypes and serial parts in industries such as machinery, aviation or automotive.
The most popular alloys in this group include materials based on MaragingSteel MS, ToolSteel 1.270, ToolSteel H13. These materials are widely used for injection molding tools, parts operating in harsh weather conditions.
The most popular alloys in this group include materials based on 316L, PH1, 17-4PH. The use of these materials is wide: from unit production to serial production across many industries. High-alloy steels are also used in medicine.
The most popular alloys from this group include materials based on IN718, IN625, IN939. These alloys are used in the applications highly impacted by temperature.
Costs and Lead Time
What affects costs and lead time in DMLS/SLM
-
 Part volume
Part volume -
 Used material
Used material -
 Used parameters (e.g. layer thickness)
Used parameters (e.g. layer thickness) -
 Bottom brackets - check other technologies without support
Bottom brackets - check other technologies without support -
 Production series size
Production series size -
 Applied postprocessing - more information in postprocessing
Applied postprocessing - more information in postprocessing -
 Choosing express execution options
Choosing express execution options
Want to optimize costs?
Want to optimize costs?
DMLS/SLM design guidelines
For the DMLS / SLM technology, we recommend the following rules:
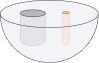
Minimum bore diameter 2 mm

Minimum wall thickness from 0.8 mm depending on the geometry
For geometries above 35 deg, the manufacturing is possible without a support structure
Provide access to areas with support to remove it
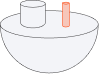
The positioning pins should be at least 2mm thick / diameter
Not sure about your design?
Not sure about your design?