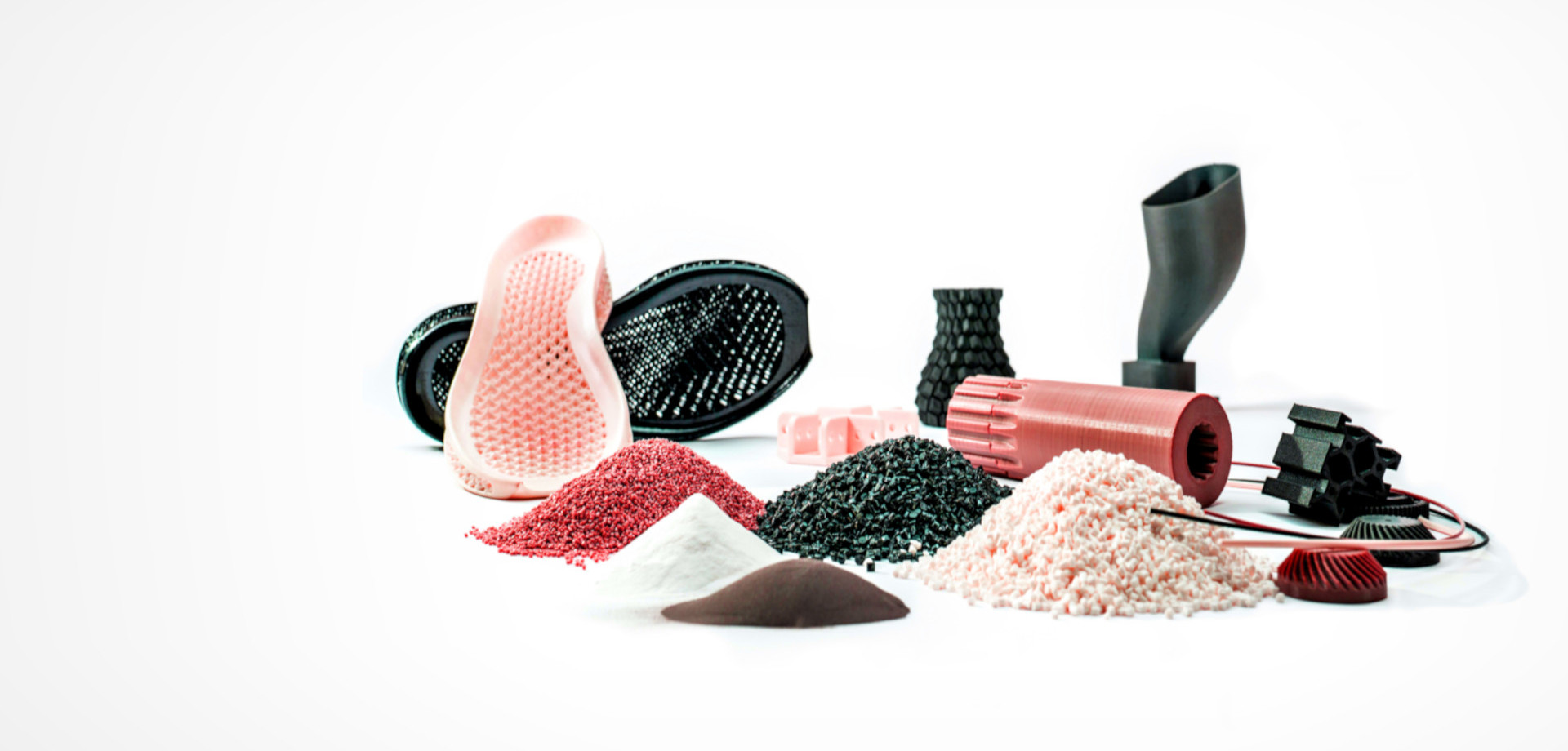
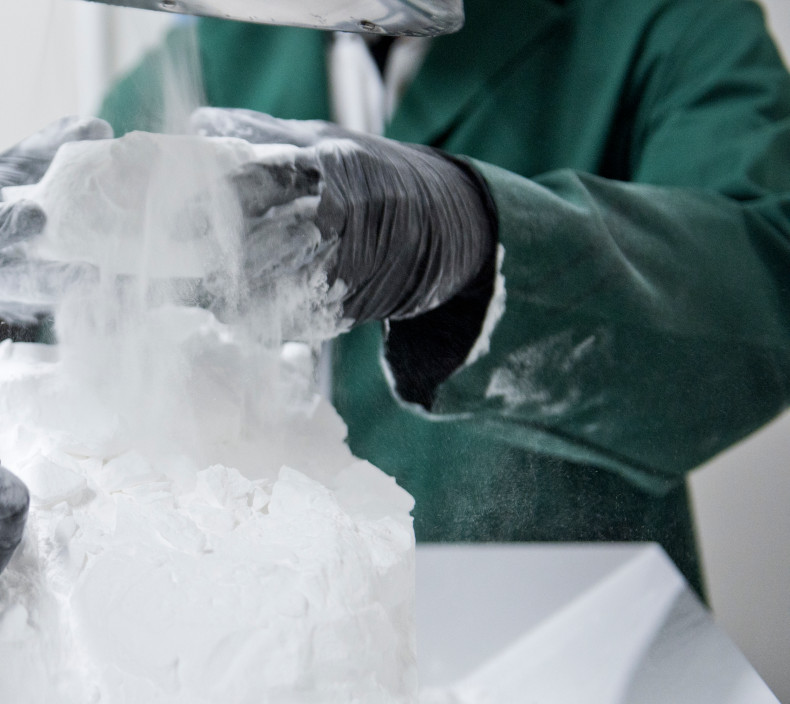
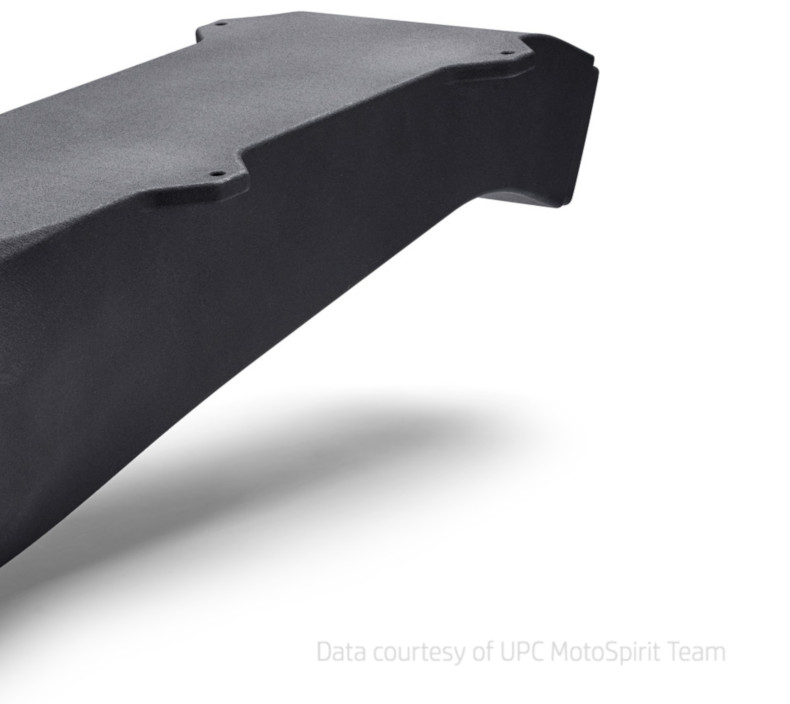
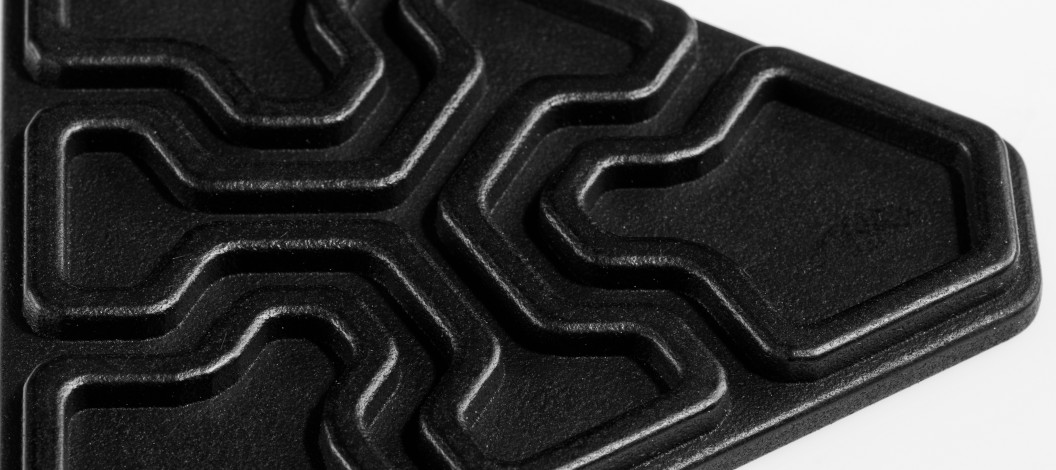
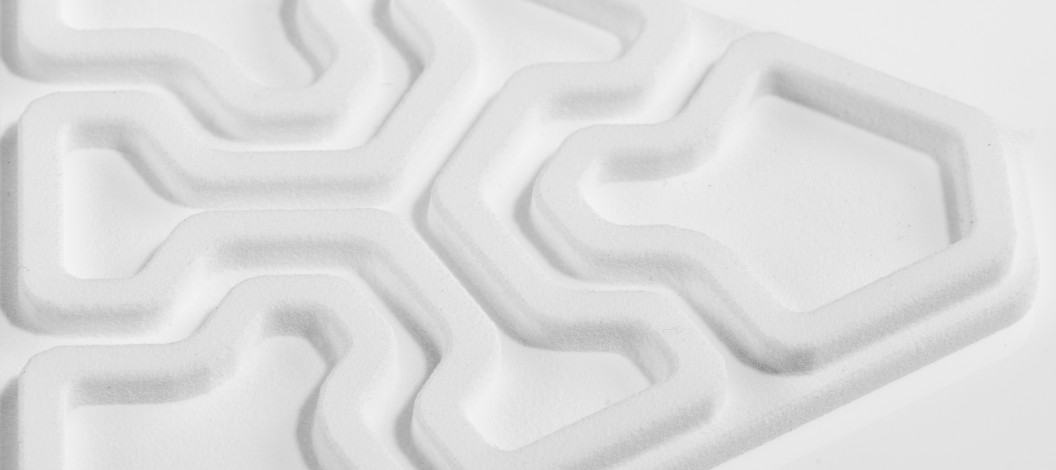
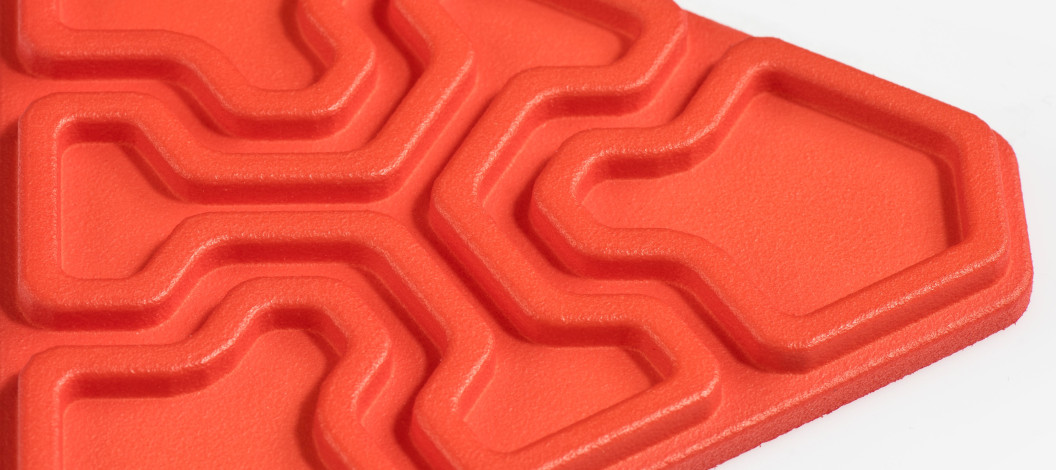
Chemical Smoothing
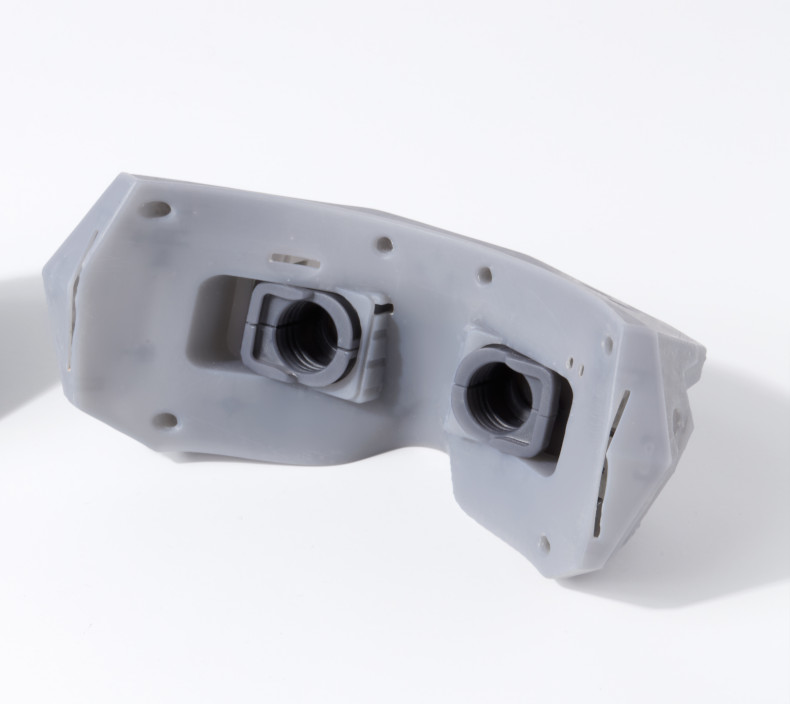
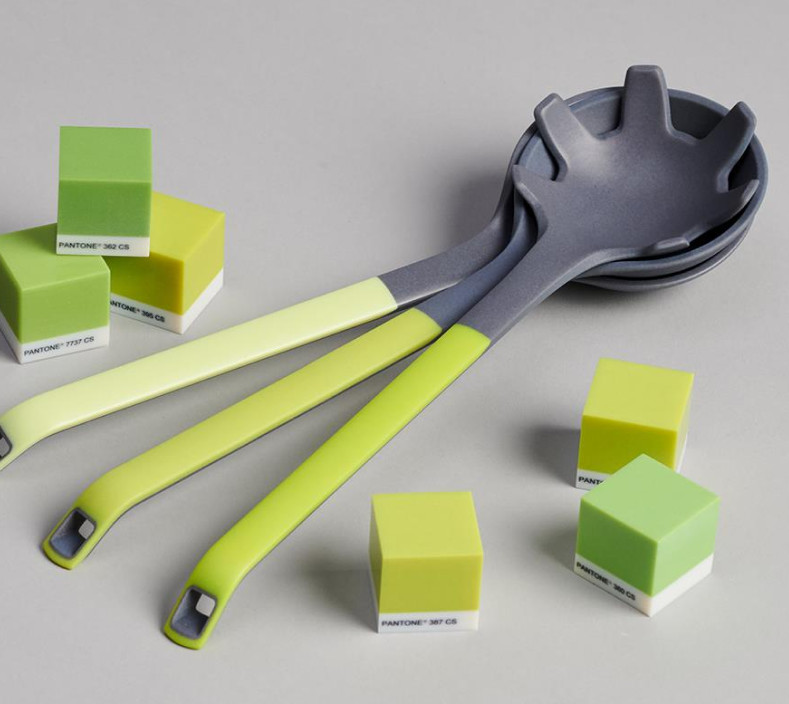
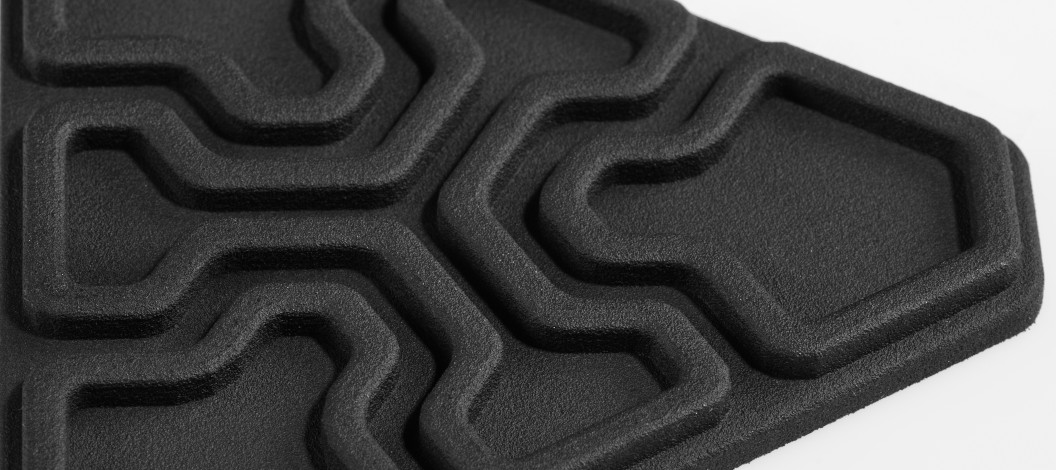
Chemical smoothing is a method used to process prints made from PA12, PA11, and TPU materials, transforming rough surfaces into perfectly smooth finishes. The process involves gently dissolving the surface of an object with the vapors of a specialized solvent. This controlled dissolution smooths the object’s surface, eliminating visible 3D printing layer lines. The result is an aesthetic, glossy surface that not only appears professional but can also enhance the mechanical and functional properties of the object.
Advantages of Chemical Smoothing:
High-Quality Finish: The primary benefit of this method is the exceptionally smooth surface it achieves.
Improved Mechanical Properties: By removing even the smallest irregularities and reducing the risk of surface defects, the process enhances the durability of the model.
Protection Against Contamination: The ultra-smooth surface is less prone to dirt accumulation and is easy to clean, making it ideal for applications where hygiene is crucial, such as in medicine or the food industry.
Production Efficiency: A quick and automated smoothing process increases productivity.
Sustainability: Minimal chemical and energy usage translates to ecological and economic benefits.